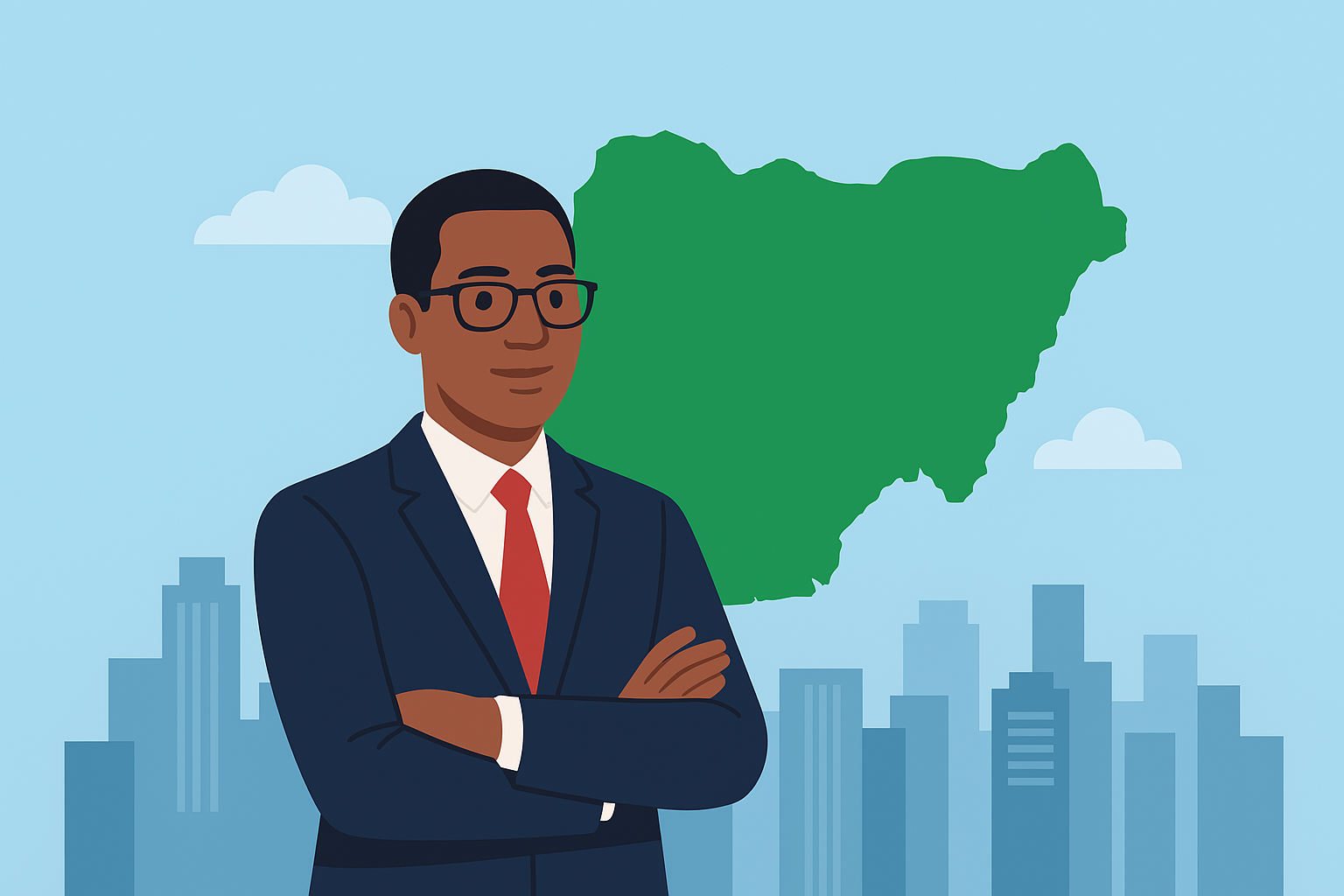
When registering or running a company in Nigeria, one of the first steps is to appoint directors. These individuals are the "mind and will" of the corporation, entrusted with steering the company toward its strategic goals while maintaining strict compliance with the law.
The Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) 2020 fundamentally redefined the rules for who can serve on a Nigerian board. Understanding these requirements is non-negotiable for every startup founder, SME owner, and investor aiming for legal compliance and effective governance.
Who Can Be a Company Director in Nigeria? Requirements under CAMA 2020 Explained
This guide provides comprehensive information on director eligibility in Nigeria under the CAMA 2020, including requirements, disqualifications, exceptions, and practical compliance tips.
Who Is a Company Director?
A director is an individual appointed to manage and direct a company’s operations, as defined in Section 244 of CAMA 2020. Directors come in three types:
Executive Directors: Handle day-to-day operations (e.g., CEO, CFO).
Non-Executive Directors: Provide oversight without daily involvement.
Independent Directors: Offer unbiased guidance, free from company ties (mandatory for public companies).
Directors owe fiduciary duties to act in good faith, avoid conflicts of interest, and work in the best interest of the company and shareholders.
Role of a Company Director
The director's role is governed by Part B, Chapter 7 (Sections 271–307) of CAMA 2020. They are more than mere figureheads; they are legally classified as:
- Agents: Acting on behalf of the company in daily business operations.
- Trustees: Safeguarding the company's assets and managing its affairs.
- Fiduciaries: Owing a high duty of care, skill, and diligence to act in good faith and in the best interests of the company and its shareholders.
Non-compliance with the duties and eligibility requirements outlined in CAMA 2020 can lead to severe consequences, including personal liability, significant fines, or even the dissolution of the company.
Why CAMA 2020 Matters for Directors
CAMA 2020, signed into law on August 7, 2020, introduced major reforms to strengthen corporate governance in Nigeria. Key updates affecting directors include:
- Single director allowed for small companies (Section 271).
- Mandatory independent directors for public companies (Section 275).
- Restrictions on multiple directorships: no more than five public company boards per person (Section 307).
- Stricter liabilities: non-compliance can result in fines up to ₦500,000 or imprisonment.
For business owners, understanding these rules is critical to avoiding CAC rejection, fines, or governance risks.
Basic Eligibility Requirements for Company Directors in Nigeria
Unlike some jurisdictions, there's no mandatory educational or professional background required; directors can come from diverse fields, as long as they meet basic criteria. Here's a breakdown:
Age Requirements:
Under CAMA 2020, a person must be at least 18 years old to qualify as a company director in Nigeria. This ensures that directors are legally competent to make binding decisions on behalf of the company.
Individuals under 18 (minors) cannot be appointed as directors.
There is no maximum age restriction, but for public companies, directors above 70 years can only be appointed or re-appointed if a special notice of their age is given (Section 282, CAMA 2020).
Mental Capacity:
Directors must be of sound mind. Section 283(a) disqualifies anyone declared mentally unfit by a court in Nigeria or abroad. This ensures rational decision-making. If a director’s mental health declines, they may vacate office under Section 284 to protect the company.
Residency and Nationality:
CAMA 2020 imposes no residency requirement. Both Nigerians and foreigners can serve as directors (Section 20). However:
Foreign directors must comply with immigration laws (e.g., CERPAC card, business permit).
If all directors are non-residents, a local company secretary is mandatory for CAC compliance.
Certain regulated sectors (e.g., banking, oil & gas) may restrict foreign participation without Nigerian Investment Promotion Commission (NIPC) approval.
This openness facilitates foreign investment, vital for Nigeria’s export-driven industries.
Shareholding Qualifications:
Directors are not required to hold shares unless the company’s Articles of Association specify otherwise (Section 277). If shares are required, directors must acquire them within two months of appointment or vacate office.
Number of Directors:
Requirements vary by company type:
Small companies: At least 1 director (Section 271).
Private companies (non-small): At least 2 directors.
Public companies: At least 3 independent directors, with no individual holding more than 5 public company directorships (Section 307).
Legal and Corporate Status:
Directors must be natural persons; corporations cannot serve as directors, though they can appoint representatives (Section 244). Multiple directorships are allowed, but conflicts of interest must be disclosed.
Disqualifications: Who Cannot Be a Director?
CAMA 2020 (Section 283) outlines strict disqualifications to protect companies from unfit leadership. Acting as a director while disqualified incurs personal liability (Section 276). Key disqualifications include:
Undischarged Bankruptcy:
An undischarged bankrupt cannot serve unless permitted by a court (Section 283(b)). This safeguards company assets, especially critical in Nigeria’s post-COVID economic recovery, where bankruptcy cases have risen.
Conviction for Fraud or Dishonesty:
Individuals convicted of fraud, dishonesty, or corporate misconduct (e.g., insider trading) within the last 10 years are disqualified if the appeal period has lapsed (Section 283(d)). This applies to convictions in Nigeria or equivalent offenses abroad, aligning with EFCC anti-corruption efforts.
Unsound Mind:
Court-declared mental incapacity disqualifies a person (Section 283(a)), assessed via medical evidence to ensure competent leadership.
Suspension or Removal:
A unique CAMA 2020 provision (Section 283(c)) disqualifies directors suspended or removed under Section 288 (e.g., for breach of duty) from all directorships. This controversial “overkill” clause deters misconduct but may penalize directors removed for non-criminal reasons.
Regulatory or Court Bans:
Directors disqualified by courts or regulators (e.g., SEC for public companies) are barred. Specific sectors may impose additional restrictions.
Public Company Independent Director Rules:
Independent directors for public companies face extra criteria (Section 275):
No employment with the company in the last three years.
No payments exceeding ₦20 million from the company.
Shareholding below 30%.
Eligibility Checklist for Directors
Use this checklist to confirm eligibility under CAMA 2020:
Age: Any age permitted (check articles for restrictions).
Mental Capacity: Not declared of unsound mind by a court.
Bankruptcy: Not an undischarged bankrupt.
Criminal Record: No unappealed fraud/dishonesty convictions in the last 10 years.
Prior Removals: Not suspended/removed from another directorship.
Shares: Meet any article-specified shareholding within 2 months.
Public Companies: Qualify as independent if required (no recent ties, low shares).
Multiple Roles: Not exceeding 5 public company directorships.
If all boxes are checked, you’re eligible. Unsure? SplashDict’s vetting services can confirm.
Why Director Eligibility Matters
Appointing an ineligible director risks:
CAC Rejection: Invalid registrations or filings.
Penalties: Fines up to ₦500,000 or imprisonment for non-compliance.
Governance Risks: Fraud, mismanagement, or shareholder disputes.
Reputational Damage: Loss of investor trust in Nigeria’s competitive market.
Proper vetting ensures compliance and strengthens your board’s credibility.
How SplashDict Helps with Director Services
As Nigeria’s leading corporate secretarial and compliance provider, SplashDict streamlines the process with comprehensive, end-to-end solutions tailored to your needs:
Director Appointments: We handle the filing of initial director appointments during company registration with the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC).
Nominee Director Services: We provide professional nominee director solutions where required, ensuring confidentiality, compliance, and business continuity.
Director Changes & Resignations: From appointment to resignation or removal, we manage the entire process of filing changes in directorship with CAC.
Update of Particulars: We file and update changes in directors’ particulars, such as name, address, phone number, gender, or other details, directly with CAC.
With SplashDict, your board remains legally compliant, properly documented, and future-ready.
Frequently asked questions
Below are answers to common questions about who can serve as a company director in Nigeria, based on the requirements of the Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) 2020.
1. Who qualifies to be a company director in Nigeria?
Any individual at least 18 years old, of sound mind, not bankrupt, and not disqualified under CAMA 2020 can be a director. Both Nigerians and foreigners are eligible.
2. Can a company (corporate entity) act as a director?
No. Only natural persons (human beings) can serve as directors under Nigerian law. Companies and organizations cannot be appointed as directors.
3. Are foreigners allowed to serve as directors in Nigeria?
Yes. Foreign nationals can serve as directors, provided they meet eligibility requirements.
4. Do directors have to be shareholders in the company?
No. Being a shareholder is not a requirement for being a director. However, a person can be both a shareholder and a director if they own shares.
5. How many directors must a Nigerian company have?
Private companies: At least 1 director. Public companies: At least 2 directors.
6. Can one person be a director in multiple companies?
Yes. Nigerian law does not limit the number of companies in which a person can serve as a director, provided they are not disqualified and can discharge their duties effectively.
7. What is the process for appointing or removing a director?
Directors are usually appointed during incorporation or later via board/shareholder resolution. Removals must follow due process under CAMA 2020 and be filed with the CAC within 14 days.
8. What are the legal duties of a director in Nigeria?
Directors must act in the best interest of the company, avoid conflicts of interest, ensure compliance with CAMA 2020, and exercise fiduciary duties of care, skill, and loyalty.
9. What happens if an ineligible person is appointed as a director?
Such an appointment is invalid, and the company risks regulatory sanctions, fines, or having its filings rejected by the CAC.
10. How does SplashDict assist with director-related services?
SplashDict helps with:
Filing initial director appointments during incorporation
Handling director changes (resignation, removal, replacement)
Updating director particulars (name, address, gender, phone, etc.)
Providing nominee director services for compliance
Keep your company records accurate by updating director details or appointments with CAC.
 Change of Company Director
Change of Company DirectorFile notice of appointment, resignation, or removal of a director with the CAC.
 Change in Particulars of Director
Change in Particulars of DirectorUpdate Director’s details (name, address, gender, phone number) with CAC.